Viral Illnesses in Children and How to Prevent Them
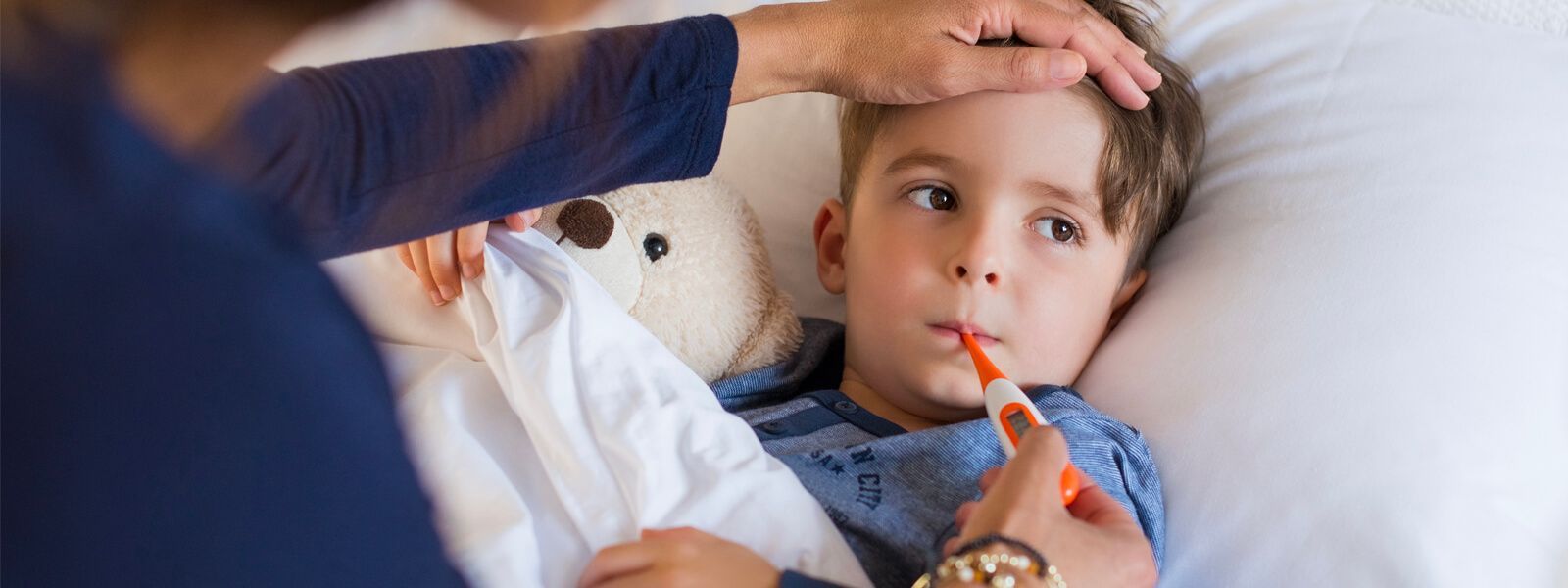
Everyone has experienced the terrible situation of staying in bed because of some viral illnesses at some point in their lives. What older people sometimes consider a moment to rest and recharge their energy, is hell for little children. Because they are in the age of discovery, exploration, and adventure. The last thing they want is for their lives to be interrupted.
Due to these times of drastic climatic changes where the flow of viruses increases, respiratory and gastrointestinal infections spread. Given this information, we introduce a guide with the most common viral illnesses in children. That way, you can recognize and prevent them at all costs. Speak to your family doctor about a personalized diagnosis and treatment.
What Are Viral Illnesses?
Some infectious illnesses are caused by microorganisms: bacteria, fungi, viruses, protozoa, among others. Most noteworthy, they are transferred through the airway (mouth) and through direct contact. Consequently, they are highly contagious.
What Are the Symptoms?
There are many types of viruses, which makes recognizing each one of their symptoms difficult. If the infection is respiratory, it is common to feel: fever, throat pain, nasal congestion, general unrest, tiredness, and coughing. Also, if they are intestinal infections, there is the presence of diarrhea, vomit, and muscle pain.
The most common are:
- Mononucleosis. A permanent virus known as mono. Symptoms include fever, constant and persistent fatigue, throat pain, muscle pain, and yellowing of the skin and eyes. Two weeks of full rest.
- Cold. A condition of the airway. Characterized by coughing, secretion, mucus, and nasal obstruction. As a result, the child has difficulty breathing. The symptoms disappear in a timeframe of seven days without leaving aftereffects.
- Measles. An infectious disease that affects unvaccinated babies and children. These appear on the inferior part of the mouth, cheeks, and palate. They extend to the face and neck. In addition, it can cause dry coughing, fever, and muscle pain. The incubation period lasts between 10 to 14 days.
- Flu. It is transmitted through the air, or through the coughing or sneezing of infected people. The symptoms appear one or two days after infection: fevers over 38°C, dry coughing, difficulty breathing, tiredness, muscle, and headaches. After seven or ten days, these symptoms should stabilize. If they persist, contact your doctor immediately.
- Child herpes. Transmitted through contact, and triggered by a fever, friction, or fatigue. The infection process lasts between 10 to 14 days. During this time, the blisters mature, break, dry, and leave scabs that fall off without leaving scars. The little one must wash his or her hands frequently so the virus does not spread.
- Mumps. A viral infection that causes an inflammation of the saliva glands and a fever. Transmitted through contact with an infected person’s saliva.
- Rubella. Considered an inoffensive disease. Characterized by a reddish rash, fever, and general unrest. Lasts between two to three weeks. While it is highly contagious its worst from one week prior to feeling any symptoms to one week after symptoms are gone.
- Chickenpox. Characterized by small rashes that are filled with a clear liquid that become yellowish. After a few days, they break and leave a scab. They can appear on the head and torso. They produce itching and high fevers in some cases.
How to Prevent Them?
First of all, wash hands frequently, especially before eating and after using the bathroom. Restrict visits of people with a cold and avoid contact with other infected children. Keep the immunization schedule complete and upgraded for the whole family. Avoid smoking inside the house or car. In conclusion, keep a clean atmosphere in the children’s rooms.
Pharmacological treatment is not administered. Except in very specific cases. That is why we recommend starting taking care at home, by providing an atmosphere with a nice temperature, as well as good hydration and nutrition. Therefore, do not hesitate to visit the doctor if necessary.